The main function of the cycle is to generate energy by oxidation of acetic acid which is produced by decarboxylation of pyruvic acid and fed into the TCA cycle. It is a common pathway of oxidative breakdown of carbohydrates fatty acids and amino acids.

Give Schematic Representation Of Kreb S Cycle
These molecules enter the matrix of a mitochondrion where they start the Krebs cycle.
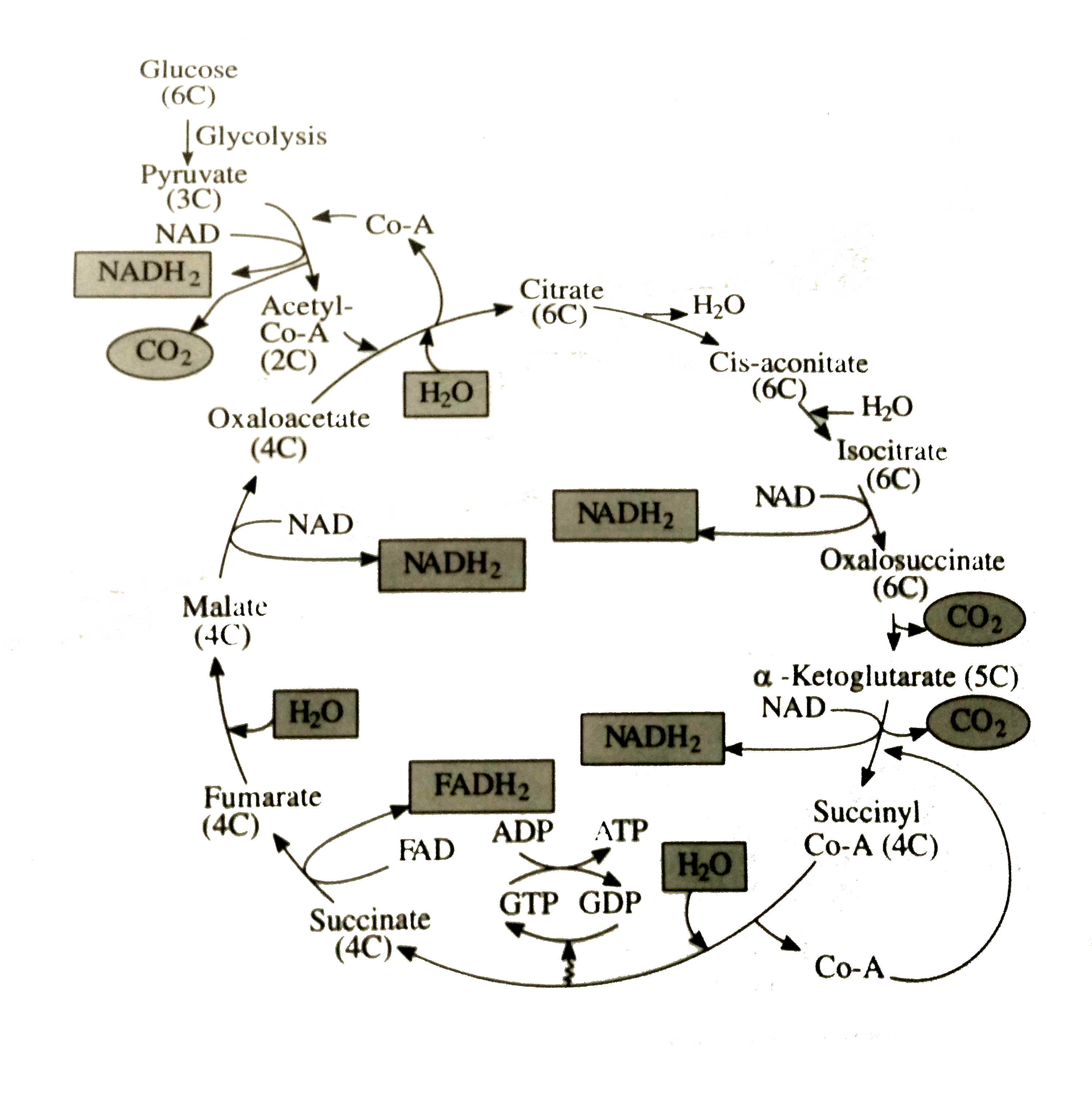
Schematic diagram of krebs cycle. Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle is one of the most important reaction sequences in biochemistry. Pyruvate is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide. Schematic Diagram of the Krebs or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.
In this article we will discuss about the functions of the Krebs cycle explained with the help of diagrams. Citric acid is a carboxylic acid containing 3 COOH groups. Citric acid is a carboxylic acid containing 3 COOH groups.
Schematic Diagram About Citric Acid Cycle Biology Biology Drawing Draw Glycolytic Pathway And Krebs Cycle Biology Sketch The Glycolytic And Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle. The Krebs cycle starts with pyruvic acid from glycolysis. The citric acid cycle - also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle TCA.
Each small circle in the diagram represents one carbon atom. Name of the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. Krebs Cycle Steps 3 And 4 Science Diagram Quizlet Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Tca Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Animation Biochemistry Usmle Step 1 Metals Promote Sequences Of The Reverse Krebs Cycle Nature.
What is the significance of juxta glomerular apparatus JGA in kidney. Simple Diagram Of The Calvin Cycle The Light Independent Krebs Citric Acid Cycle Steps By Steps Explanation 1 Schematic Representation Of The Calvin Cycle The Photosynthesis Atp And Adp Cycle Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Biochemistry Britannica Krebs Cycle Simple And Easier To Read Biochemistry Krebs Cycle. Krebs cycle is the major pathway for the synthesis of coenzyme and controlled release of energy during respiration.
Can you suggest any reason for its sigmoidal Pattern. This cycle is also called citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid. When measuring the energy production of the Krebs cycle the output is measured in molecules of ATP Adenosine triphosphate per molecule of glucose.
Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. The Krebs cycle is simply another name for the Citric Acid Cycle so named for the researcher who identified the complete cycle in 1937. These cycle diagrams are designed to guide you in studying the acid cycle.
Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. Hence this cycle is also called as tri carboxylic acid cycle or TCA cycle.
The Krebs cycle is the primary metabolic pathway through which aerobic energy is released from carbohydrates proteins and fats in a useable form. It is an eight-step process. In the second step citrate is converted into its isomer isocitrate.
It produces GTP which is important for signal. Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic condition. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate.
Define oxygen dissociation curve. This cycle is also citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid. The vector stencils library Citric acid cycle TCA cycle contains 26 symbols of metabolites for drawing metabolic pathway maps and biochemical shematic diagrams of the citric acid cycle TCA cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle Krebs cycle and diagrams of metabolism processes.
The reactions of the cycle where synthesis of adenosine triphosphate ATP is coupled with the electron transport chain oxidative phosphoryla- tion are shown. The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate coenzyme A. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes.
Krebs Cycle Steps. Q5 Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. This Krebs cycle is the oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO 2 and water.
The TCA cycle or Krebs cycle after H. Q7 Distinguish between the following. The reactions that occur next are shown in Figure below.
You can watch an animated version at this link. A Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration b. The cycle operates in aerobic organisms including animals plants and microorganisms.
Amino acid enters the Krebs cycle directly as glutamate and aspartate after their deamination. Krebs is a cyclic sequence of reactions through which pyruvic acid produced in the EMP and EDP is oxidized. This cycle was first described by Krebs in 1936.